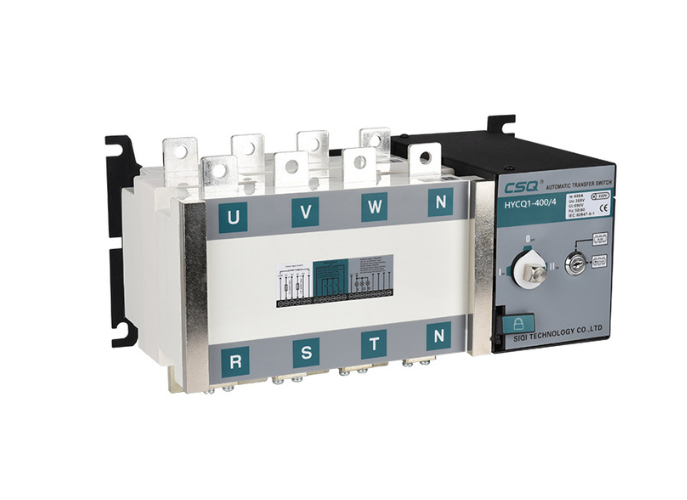
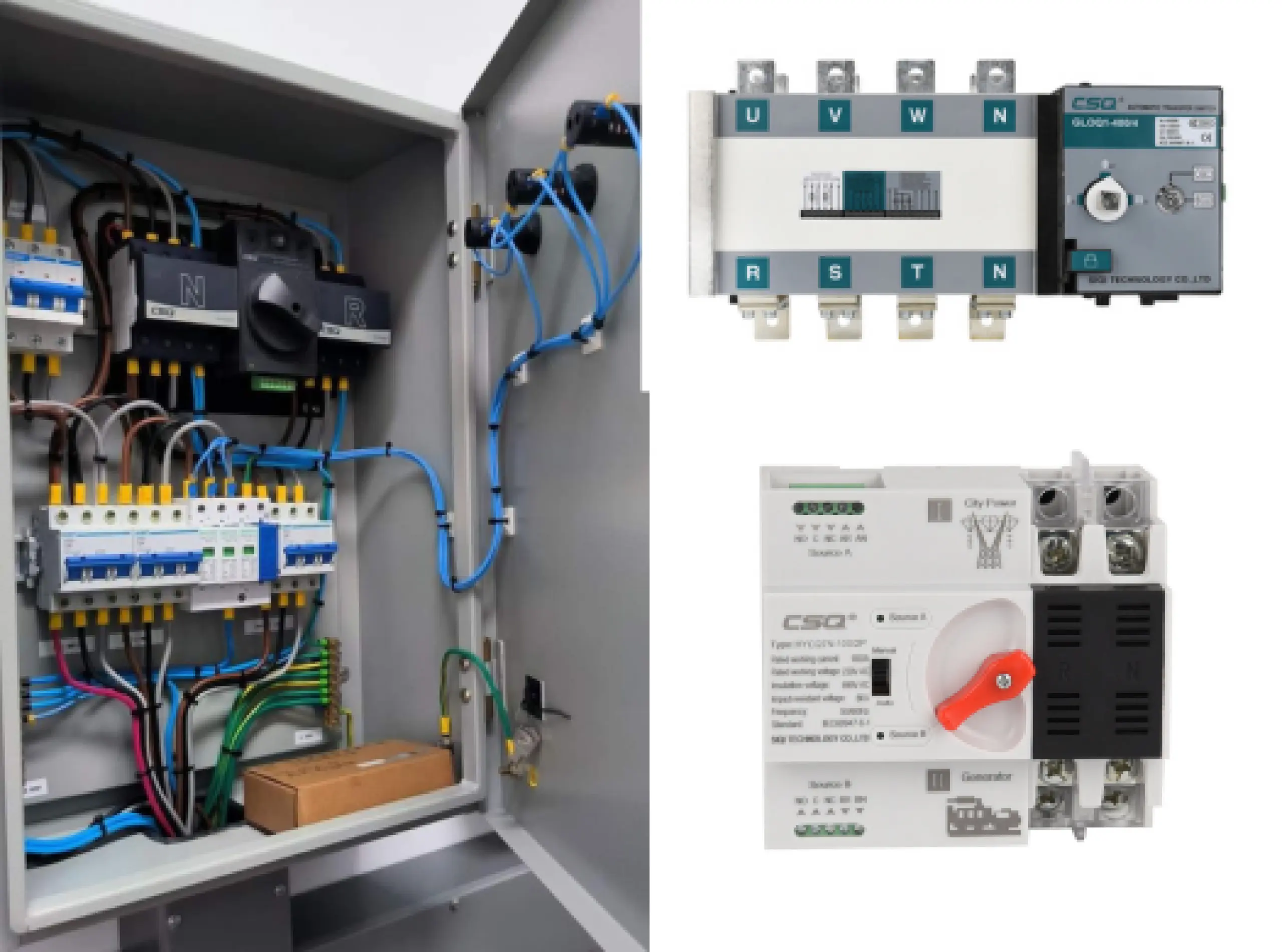
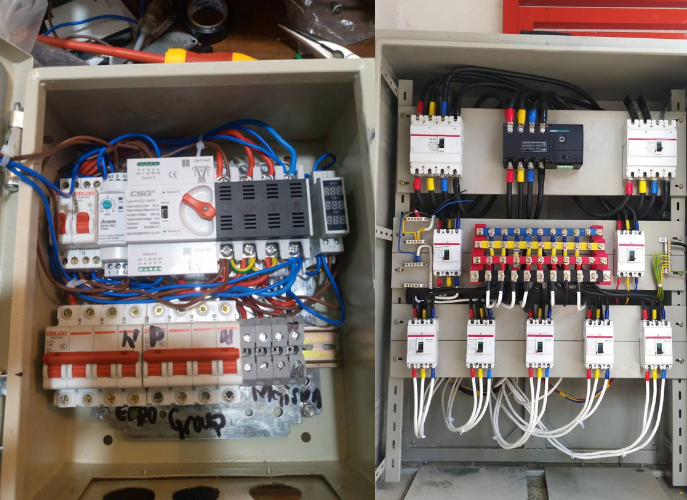
What Is A Generator Automatic Transfer Switch?
The Generator Automatic Transfer Switch is a pivotal element in modern power management, offering automatic, reliable, and safe transitions between power sources across various settings. Its ability to provide uninterrupted power supply enhances operational continuity and safety, making it indispensable in many applications.
What are Generator Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS)?
A Generator Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is a critical component in power management systems, designed to ensure a seamless transition between a primary power source and a backup generator. The ATS detects power failures and automatically switches to the generator, maintaining power continuity. Once the primary power source is restored, the ATS transfers the load back to it and shuts down the generator. This automated process eliminates the need for manual intervention, enhancing the reliability and convenience of power systems.
The importance of an ATS in power management cannot be overstated. In scenarios where continuous power supply is crucial, such as in hospitals, data centers, and industrial operations, an ATS ensures that there are no interruptions that could lead to significant losses or even life-threatening situations. By automatically managing the transition between power sources, the ATS helps in minimizing downtime, protecting sensitive equipment, and maintaining operational efficiency. It also enhances safety by preventing electrical hazards that might occur during manual switching.
ATS devices are used across a wide range of applications and settings. In residential settings, they provide homeowners with peace of mind by ensuring that essential appliances and systems remain operational during power outages. In commercial buildings, ATS systems keep businesses running smoothly, avoiding costly disruptions. Industrial facilities rely on ATS for the continuity of production processes, preventing financial losses and ensuring safety compliance. Moreover, in critical infrastructure such as healthcare facilities, the reliable operation of ATS can be a matter of life and death, ensuring that medical equipment remains functional and patient care is not compromised.

Components of an Automatic Transfer Switch
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) comprises several critical components that work together to ensure a seamless transition between the main power source and the backup generator. Understanding these components is essential for grasping how an ATS operates and maintains uninterrupted power supply.
1. Main Power Source (Utility)
The primary component of an ATS system is the main power source, typically the utility power supplied by the local electricity grid. This source is the default provider of electrical power to the system, ensuring that all connected devices and equipment receive the necessary electricity during normal conditions. The ATS constantly monitors the utility power for any disruptions or irregularities. When the utility power is stable and within acceptable parameters, the ATS ensures that the load is supplied from this source, providing reliable and cost-effective electricity.
2. Backup Power Source (Generator)
The backup power source, usually a generator, is activated when the main power source fails. Generators can be powered by various fuels, such as diesel, natural gas, or propane, and are designed to provide electricity when the utility power is unavailable. The generator remains on standby, ready to start and supply power immediately upon detection of a power outage. The ATS manages the initiation and shutdown of the generator, ensuring that it only operates when necessary, thus conserving fuel and reducing wear and tear on the equipment.
3. Transfer Switch Mechanism
The heart of the ATS is the transfer switch mechanism, which facilitates the changeover from the main power source to the backup generator and vice versa. This mechanism includes electrical contacts and a mechanical or electronic actuator that physically switches the load between the two power sources. When a power outage is detected, the transfer switch disconnects the load from the utility and connects it to the generator. Once the utility power is restored and stabilized, the switch transfers the load back to the utility and shuts down the generator. This process is designed to be smooth and quick, minimizing any interruption to the power supply.
4. Control Panel and Sensors
The control panel and sensors are essential for the automated operation of the ATS. The control panel houses the electronics and circuitry that manage the transfer switch mechanism, monitor the status of both power sources, and communicate with the generator. Sensors detect various parameters, such as voltage, frequency, and phase alignment, ensuring that the power sources are compatible and that the transition occurs without damaging the connected equipment. Advanced ATS models may include digital displays, programmable settings, and remote monitoring capabilities, allowing for greater control and flexibility in managing power transitions.

How a Generator Automatic Transfer Switch Works
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is designed to ensure a seamless transition between utility power and backup generator power, providing uninterrupted electricity to critical systems. This process involves several key steps, which are essential for understanding how an ATS maintains continuous power supply.
1. Normal Operation with Utility Power
During normal operation, the ATS continuously monitors the incoming utility power, which is the primary source of electricity. Under these conditions, the ATS ensures that the electrical load, such as household appliances, commercial equipment, or industrial machinery, is supplied directly from the utility grid. The ATS remains in a standby mode, with the transfer switch positioned to connect the load to the utility power. This configuration ensures that the system operates efficiently and cost-effectively, using the reliable and stable power provided by the utility company.
2. Detection of Power Outage
The ATS is equipped with sensors and monitoring systems that detect any irregularities or failures in the utility power supply. When a power outage occurs, the ATS quickly identifies the loss of utility power by sensing changes in voltage, frequency, or phase. This detection is almost instantaneous, enabling the ATS to respond promptly to the disruption. The rapid detection is crucial for minimizing the duration of power loss and preventing damage to sensitive electronic equipment.
3. Switching to Generator Power
Activation of the Generator
Upon detecting a power outage, the ATS sends a signal to the backup generator to start. The generator, which has been in standby mode, begins its startup sequence. Depending on the type of generator, this process can take a few seconds to a minute. The generator must reach its optimal operating speed and stabilize its output voltage and frequency before taking over the load.
Transfer of Electrical Load
Once the generator is running smoothly and producing stable power, the ATS initiates the transfer of the electrical load from the utility power to the generator. The transfer switch mechanism disconnects the load from the utility and connects it to the generator. This transition is designed to be seamless, ensuring that the connected equipment experiences minimal disruption. The entire process is automated, requiring no manual intervention, which enhances safety and reliability.
4. Reverting to Utility Power
Restoration of Utility Power
The ATS continues to monitor the utility power supply even while the generator is in operation. When the utility power is restored, the ATS detects the return of stable and reliable utility electricity. However, the ATS does not immediately switch back to the utility power; instead, it follows a predefined sequence to ensure a smooth transition.
Delay and Verification
Before transferring the load back to the utility power, the ATS waits for a predetermined delay period. This delay allows the utility power to stabilize and ensures that the restoration is not temporary or subject to further outages. During this period, the ATS verifies that the utility power parameters (voltage, frequency, and phase) are within acceptable limits.
Switching Back to Utility Power
After the delay and verification process, the ATS initiates the transfer of the electrical load back to the utility power. The transfer switch mechanism disconnects the load from the generator and reconnects it to the utility supply. This transition is carefully managed to avoid any electrical surges or interruptions. The ATS ensures that the load is securely connected to the utility power before shutting down the generator.
5. Shutdown of Generator
Once the load has been successfully transferred back to the utility power, the ATS sends a signal to the generator to begin its shutdown sequence. The generator gradually reduces its output and comes to a complete stop. The ATS returns to its standby mode, continuously monitoring the utility power and ready to respond to any future outages. This automated process ensures that the generator is only used when necessary, conserving fuel and reducing wear and tear.
Types of Automatic Transfer Switches
Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) come in various types, each designed to cater to specific needs and applications. Understanding the differences between these types can help in selecting the appropriate ATS for a given setting.
1. Open Transition ATS
Open Transition ATS, also known as break-before-make switches, momentarily disconnect the load from the power source during the transfer process. This brief disconnection, usually lasting a fraction of a second, ensures that there is no overlap between the utility and generator power. One of the main advantages of an open transition ATS is its simplicity and reliability. These switches are less complex and generally more cost-effective compared to other types, making them a popular choice for many applications. Additionally, because there is no overlap of power sources, there is less risk of electrical faults or damage.
Open Transition ATS are suitable for environments where a brief interruption of power is acceptable. They are commonly used in residential settings, small commercial buildings, and non-critical industrial applications. In these scenarios, the brief power loss does not significantly impact operations or cause harm to sensitive equipment.
2. Closed Transition ATS
Closed Transition ATS, or make-before-break switches, ensure that there is no interruption in power supply by briefly connecting the utility and generator power sources simultaneously during the transfer process. This overlapping phase, which typically lasts a few milliseconds, provides a seamless transition with no noticeable interruption to the load. The primary advantage of a closed transition ATS is the continuous power supply, which is crucial for operations where even a momentary loss of power can be disruptive or damaging. This type of ATS also helps in maintaining the stability and reliability of the power system.
Closed Transition ATS are ideal for critical applications where power continuity is essential, such as hospitals, data centers, and high-stakes industrial processes. These environments cannot tolerate even a brief power interruption, making the seamless transition provided by closed transition ATS indispensable.
3. Static Transfer Switches
Static Transfer Switches (STS) use power electronics instead of mechanical components to transfer the load between power sources. This allows for extremely fast switching times, often in the range of milliseconds, ensuring virtually uninterrupted power. The use of solid-state devices means there are no moving parts, which reduces wear and tear and increases reliability. Additionally, STS can offer better control over power quality and are capable of handling higher power densities.
Static Transfer Switches are used in applications requiring ultra-fast and reliable power switching, such as advanced data centers, telecommunications infrastructure, and high-tech manufacturing facilities. These environments demand minimal downtime and maximum power quality, which STS are well-equipped to provide.
4. Manual Transfer Switches (Comparison)
Manual Transfer Switches require an operator to manually switch the load from one power source to another. Unlike automatic transfer switches, they do not detect power outages or initiate the transfer process automatically. Manual switches are simpler and less expensive, but they require human intervention, which can lead to longer power interruptions and increased risk of operator error.
In comparison to automatic transfer switches, manual transfer switches are more suitable for situations where power outages are infrequent or where a brief power interruption is not critical. They are often used in smaller residential setups, remote facilities, or backup systems where cost is a significant consideration and immediate power continuity is not as crucial.
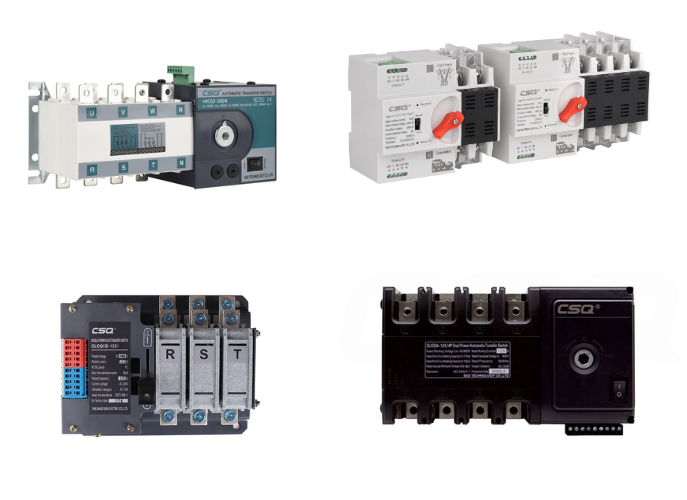

Benefits of Using a Generator ATS
Using a Generator Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) offers numerous advantages, making it an indispensable component in various power management systems. These benefits range from ensuring continuous power supply to enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
1. Uninterrupted Power Supply
One of the most significant benefits of a Generator ATS is its ability to provide an uninterrupted power supply. The ATS automatically detects a power outage and seamlessly switches to the backup generator without any noticeable interruption to the load. This capability is crucial for critical applications such as hospitals, data centers, and industrial processes, where even a brief loss of power can lead to severe consequences, including data loss, equipment damage, and operational disruption. By ensuring continuous power, the ATS maintains the smooth functioning of essential services and systems, safeguarding against the risks associated with power outages.
2. Enhanced Safety and Reliability
Generator ATS enhances the safety and reliability of power systems. The automatic operation reduces the need for manual intervention, which can be prone to human error and potentially hazardous, especially during severe weather conditions or in emergency situations. The ATS ensures that the transition between power sources is performed safely and efficiently, minimizing the risk of electrical faults, surges, or other issues that could harm personnel or damage equipment. Additionally, modern ATS units are equipped with advanced monitoring and diagnostic features, enabling proactive maintenance and early detection of potential problems, further enhancing system reliability.
3. Convenience and Automation
The convenience and automation provided by a Generator ATS are significant advantages for both residential and commercial users. The ATS automatically manages the switching process, eliminating the need for manual oversight and allowing for a hands-off approach to power management. This automation is particularly beneficial in settings where immediate response to power outages is critical, such as in healthcare facilities or security systems. Users can be assured that their backup power system will activate and deactivates as needed without requiring their intervention, providing peace of mind and allowing them to focus on other important tasks.
4. Reduced Downtime and Operational Continuity
Reducing downtime and ensuring operational continuity are paramount in many industries and applications. A Generator ATS minimizes the duration of power interruptions by quickly switching to the backup generator when an outage occurs and just as efficiently returning to utility power once it is restored. This swift response helps maintain the continuity of operations, reducing the financial and productivity losses associated with power downtime. For businesses, this means maintaining customer service levels, protecting critical data, and ensuring that production processes continue without costly interruptions. For residential users, it ensures that essential household systems, such as heating, cooling, and refrigeration, continue to operate during power outages.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and regular maintenance of a Generator Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) are essential to ensure its reliable operation and longevity. These practices help prevent system failures, reduce downtime, and maintain the safety and efficiency of the power management system.
1. Professional Installation Requirements
Installing an ATS requires professional expertise due to the complexity and importance of the system. Certified electricians or specialized technicians should carry out the installation to ensure compliance with electrical codes and standards. Professional installation includes selecting the appropriate ATS type and size based on the load requirements and the generator's capacity. Proper wiring and grounding are crucial to prevent electrical hazards. The installation process also involves integrating the ATS with both the utility power source and the backup generator, which requires precise connections and calibration to ensure seamless operation. Additionally, professionals ensure that all safety protocols are followed, including the installation of surge protectors and circuit breakers, to safeguard the system from potential faults.
2. Regular Testing and Maintenance Procedures
Regular testing and maintenance are vital for the optimal performance of an ATS. Routine inspections should be conducted to check for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to the components. The ATS should be tested periodically to ensure that it correctly detects power outages and transfers the load to the generator without issues. This includes simulating power outages to verify the automatic switch to the generator and back to utility power. Regular maintenance also involves checking the connections, cleaning the components, and updating the control software if applicable. Ensuring that the generator is well-maintained and fuel levels are adequate is also part of the overall maintenance plan. These procedures help identify and address potential problems before they lead to system failures.
3. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite regular maintenance, issues can still arise with an ATS. Common problems include failure to switch to the generator, delayed switching, or the generator not starting. Troubleshooting these issues often starts with checking the power connections and ensuring that the ATS is receiving the correct signals from both the utility and the generator. Issues with the control panel or sensors can cause the ATS to malfunction, so verifying the integrity and functionality of these components is essential. If the generator fails to start, it may be due to fuel supply issues, battery problems, or mechanical faults. In such cases, inspecting the generator and performing necessary repairs or replacements is crucial. Consulting the ATS manual and seeking professional assistance when encountering persistent or complex issues can prevent further complications and ensure the system operates as intended.
Applications of Generator Automatic Transfer Switches
Generator Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) are versatile devices used across various sectors to ensure continuous power supply during utility outages. They play a crucial role in maintaining operational efficiency and safety in different environments, each with unique power needs.
1. Residential Use
In residential settings, a Generator ATS ensures that essential household systems, such as lighting, heating, cooling, and refrigeration, remain operational during power outages. Homeowners rely on ATS to automatically switch to backup generator power, providing uninterrupted electricity for vital appliances and systems. This is particularly important in regions prone to frequent storms or power disruptions. By maintaining power continuity, an ATS enhances the comfort and safety of residents, preventing food spoilage, ensuring security systems remain active, and allowing critical medical devices to operate without interruption.
2. Commercial Buildings
Commercial buildings, such as office complexes, retail stores, and hotels, benefit significantly from the use of Generator ATS. These switches ensure that business operations can continue smoothly during power outages, preventing financial losses and maintaining customer service levels. In an office setting, an ATS supports uninterrupted IT operations, protects data integrity, and ensures that communication systems remain functional. Retail stores can keep their lights, cash registers, and security systems running, avoiding downtime that could lead to lost sales and compromised security. For hotels, an ATS guarantees guest comfort and safety by keeping essential services such as elevators, lighting, and heating/cooling systems operational.
3. Industrial Facilities
Industrial facilities often have critical power needs due to the nature of their operations, which can include manufacturing processes, chemical production, and heavy machinery. A Generator ATS in an industrial setting ensures that production lines and essential systems continue to operate during power outages, minimizing downtime and preventing significant financial losses. The ability to automatically switch to backup power protects sensitive equipment from damage caused by sudden power loss and allows facilities to maintain safety protocols. In industries where power continuity is vital for maintaining product quality or preventing hazardous situations, an ATS is indispensable.
4. Healthcare and Critical Infrastructure
In healthcare and critical infrastructure settings, the reliability of power supply can be a matter of life and death. Hospitals, clinics, and emergency response facilities depend on Generator ATS to keep critical medical equipment, life support systems, and lighting operational during power outages. An ATS ensures that there is no disruption in the care provided to patients, maintaining the functionality of ventilators, monitors, and other essential devices. In critical infrastructure such as water treatment plants, transportation hubs, and communication networks, an ATS guarantees that operations continue without interruption, safeguarding public health and safety. The seamless transition to backup power provided by an ATS is crucial for maintaining the reliability and efficiency of these essential services.
Considerations When Choosing an ATS
Selecting the right Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) for your needs involves several critical factors. Each consideration ensures that the ATS functions effectively and reliably, meeting the specific requirements of your power management system.
1. Power Requirements and Load Capacity
One of the foremost considerations when choosing an ATS is understanding your power requirements and load capacity. It's essential to determine the total electrical load that the ATS will need to handle. This includes all connected devices and systems that require power during an outage. The ATS must be capable of managing the peak load to prevent overloads and ensure seamless operation. Overestimating the load capacity can lead to unnecessary expenses, while underestimating it can result in system failures and damage to equipment. Therefore, a precise calculation of power needs is crucial for selecting an appropriately sized ATS.
2. Compatibility with Generator and Utility Systems
Compatibility with both the generator and utility systems is another vital factor. The ATS must be compatible with the generator's power output and the specifications of the utility supply. This includes matching the voltage, frequency, and phase requirements. Additionally, the ATS should be compatible with the generator’s starting mechanism and control systems to ensure seamless communication and operation. Verifying compatibility helps in preventing operational issues and ensures that the transfer switch can efficiently manage the transition between power sources without causing electrical faults or interruptions.
3. Installation Environment and Space
The installation environment and available space significantly influence the choice of an ATS. Consider the physical dimensions of the ATS and the space available for installation. The environment, whether it is indoors or outdoors, will determine the type of enclosure needed to protect the ATS from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures. Adequate ventilation and accessibility for maintenance are also crucial. Ensuring that the ATS fits well within the designated space and is protected from environmental hazards will enhance its longevity and reliability.
4. Budget and Cost Factors
Budget and cost considerations play a significant role in selecting an ATS. While it's important to choose an ATS that meets all technical requirements, it must also fit within the budget constraints. Costs can vary widely based on the type and features of the ATS. It is essential to balance cost with reliability and functionality. Investing in a high-quality ATS might involve higher initial costs but can save money in the long run by reducing maintenance expenses and avoiding costly downtime. Additionally, considering the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and potential upgrades, provides a clearer picture of the financial commitment involved.
5. Compliance with Regulations and Standards
Compliance with local regulations and industry standards is a non-negotiable aspect of choosing an ATS. The ATS must meet the relevant electrical codes and safety standards to ensure it operates safely and legally. This includes compliance with standards set by organizations such as the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Ensuring compliance not only guarantees safety and reliability but also avoids legal issues and potential fines. It also often influences insurance premiums and coverage, as compliant systems are considered lower risk.

Conclusion
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is a vital component in modern power management systems, ensuring the seamless transfer of power between utility and backup generators during outages. It continuously monitors the power supply, detects outages, and automatically switches to a backup power source, providing uninterrupted power. By automating this process, an ATS eliminates the need for manual intervention, enhancing both convenience and safety. Its ability to maintain continuous power supply is crucial for protecting sensitive equipment, maintaining operational efficiency, and ensuring safety in various settings, from residential homes to critical infrastructure.
The role of an ATS in ensuring reliable power supply cannot be overstated. Its importance spans across multiple sectors, including residential, commercial, industrial, and healthcare. In each of these areas, the ATS safeguards against the detrimental effects of power outages, such as operational downtime, financial loss, and safety hazards. The reliability and efficiency provided by an ATS make it an indispensable tool for any setting where continuous power is essential. By reducing the risks associated with power interruptions, an ATS enhances the resilience and stability of power systems, ensuring that critical operations can proceed without disruption.
Given its critical role in maintaining power continuity, it is highly encouraged to consider the implementation of an ATS in any application where reliable power is crucial. Whether it’s for ensuring the comfort and safety of a home, maintaining business operations, supporting industrial processes, or protecting lives in healthcare facilities, an ATS provides a robust solution for power management. Investing in a suitable ATS can offer peace of mind, knowing that power supply will remain consistent and reliable, regardless of external conditions. For those in environments where power stability is not just a convenience but a necessity, an ATS is an invaluable asset.
CSQ Electric Generator Automatic Transfer Switch
CSQ Electric offers a range of reliable and efficient Generator Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) designed to ensure uninterrupted power supply in various applications. Our ATS solutions are engineered with precision and built to meet the highest quality, safety, and reliability standards.
With CSQ Electric Generator ATS, you can rest assured that your critical systems and operations remain protected during utility power outages. Our ATS units have advanced monitoring and control features, allowing seamless transitions between utility and backup power sources. Whether for residential, commercial, industrial, or healthcare applications, CSQ Electric ATS delivers unparalleled performance and peace of mind.
Backed by our commitment to excellence and customer satisfaction, CSQ Electric provides comprehensive support throughout the ATS selection, installation, and maintenance process. Our team of experts is dedicated to helping you find the perfect ATS solution tailored to your specific needs and requirements.
Choose CSQ Electric Generator Automatic Transfer Switches for reliable power management solutions that keep your operations running smoothly, even in unexpected power disruptions. Experience the reliability and efficiency of CSQ Electric ATS and ensure continuous power supply for your critical applications.
Read More: What Is ATS Electrical System?
Popular CSQ Electric Products
Get Price of Low-Voltage Electrical Products
Power Distribution System
- Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS)
- Manual Transfer Switches (MTS)
- Load Break Switches
- Fuse Switch Disconnector
- Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker With Overcurrent Protection (RCBO)
View All→
Industrial Control System
- Time Relays
- Monitoring Relays
- Other Relays
- AC Contactors
- Motor Control And Protection
- Thermal Overload Relay
View All→

Headquarter:
No.198, Wei 3rd Road, Economic Development Zone of Yueqing, Wenzhou City, China
Hangzhou Branch:
1601-3A, Unit 1, Building 1, Ruiling The World, Xiaoshan District, Hangzhou City, China
Copyright ©Siqi Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.